Next: 7.9 The Kauffman Polynomial Up: 7 Invariants Previous: 7.7 The A2 Invariant Contents Index
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
Next: 7.9 The Kauffman Polynomial
Up: 7 Invariants
Previous: 7.7 The A2 Invariant
Contents
Index
The HOMFLY-PT polynomial ![]() (see [HOMFLY]
and [PT]) of a knot or link
(see [HOMFLY]
and [PT]) of a knot or link ![]() is defined by the skein relation
is defined by the skein relation
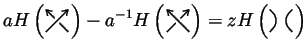
KnotTheory` knows about the HOMFLY-PT polynomial:
|
In[2]:= ?HOMFLYPT
In[3]:= HOMFLYPT::about
|
Thus, for example, here's the HOMFLY-PT polynomial of the knot
![]() :
:
In[4]:= | K = Knot[8, 1]; |
In[5]:= | HOMFLYPT[Knot[8, 1]][a, z] |
Out[5]= | -2 4 6 2 2 2 4 2 a - a + a - z - a z - a z |
It is well known that HOMFLY-PT polynomial specializes to the Jones
polynomial at ![]() and
and
![]() and to the Conway
polynomial at
and to the Conway
polynomial at ![]() . Indeed,
. Indeed,
In[6]:= | {Expand[HOMFLYPT[K][1/q, Sqrt[q]-1/Sqrt[q]]], Jones[K][q]} |
Out[6]= | -6 -5 -4 2 2 2 2
{2 + q - q + q - -- + -- - - - q + q ,
3 2 q
q q
-6 -5 -4 2 2 2 2
> 2 + q - q + q - -- + -- - - - q + q }
3 2 q
q q |
In[7]:= | {HOMFLYPT[K][1, z], Conway[K][z]} |
Out[7]= | 2 2
{1 - 3 z , 1 - 3 z } |
In our parametirzation of the ![]() link invariant, it satisfies
link invariant, it satisfies
In[8]:= | L = Link[5, Alternating, 1]; |
In[9]:= | Simplify[{
(-1)^(Length[Skeleton[L]]-1)(q^2+1+1/q^2)HOMFLYPT[L][1/q^3, q-1/q],
A2Invariant[L][q]
}] |
Out[9]= | -12 -8 -6 2 -2 2 4 6
{2 - q + q + q + -- + q + q + q + q ,
4
q
-12 -8 -6 2 -2 2 4 6
> 2 - q + q + q + -- + q + q + q + q }
4
q |