$\renewcommand{\Re}{\operatorname{Re}}$ $\renewcommand{\Im}{\operatorname{Im}}$ $\newcommand{\erf}{\operatorname{erf}}$ $\newcommand{\dag}{\dagger}$ $\newcommand{\const}{\mathrm{const}}$ $\newcommand{\arcsinh}{\operatorname{arcsinh}}$
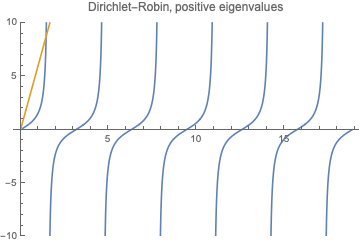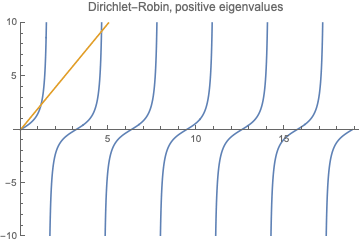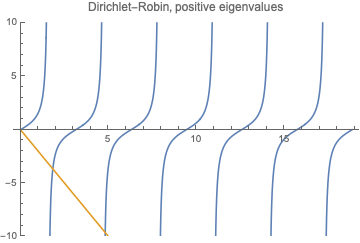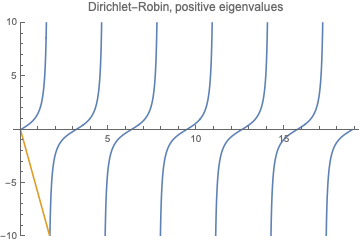
For boundary value problem \begin{align} &X''+\lambda X =0\\[3pt] &X|_{x=0}=0,\qquad (X'+\beta X)(l)=0 \end{align} let us find positive eigenvalues $\lambda=k^2$ ($k>0$) first. We have $$X= A\cos(k x) +B\sin (k x). $$ Then $A=0$ and \begin{equation} \tan (k l)=-\frac{k}{\beta}. \end{equation}
Solve it graphically:

Let us find negative eigenvalues $\lambda=-k^2$ ($k>0$). We have $$X= A\cosh(k x) +B\sinh (k x). $$ Then $A=0$ and \begin{equation} \tan (k l)=-\frac{k}{\beta}. \end{equation} \begin{equation} \tanh (kl)=-\frac{k}{\beta}. \end{equation}
Solve it graphically:
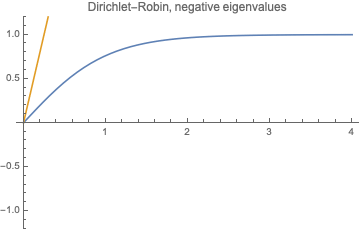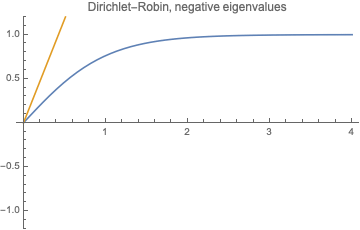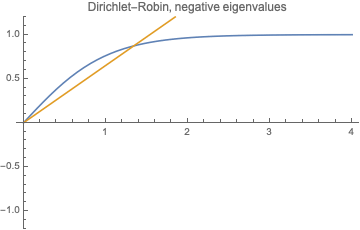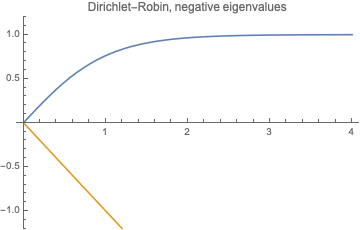
We see that there is just one positive root as $\beta <-1/l$, and no positive roots at all as $\beta\ge -1/l$.
For boundary value problem \begin{align} &X''+\lambda X =0\\[3pt] &X'|_{x=0}=0,\qquad (X'+\beta X)(l)=0 \end{align} let us find positive eigenvalues $\lambda=k^2$ ($k>0$) first. We have $$ X= A\cos(k x) +B\sin (k x). $$ Then $B=0$ and \begin{equation} \tan (k l)=\frac{\beta}{k}. \end{equation}
Solve it graphically:

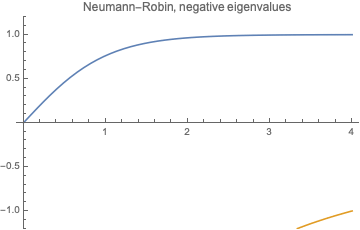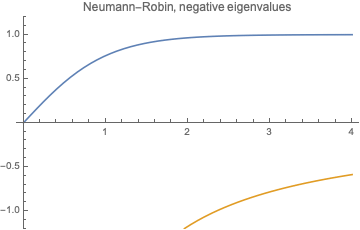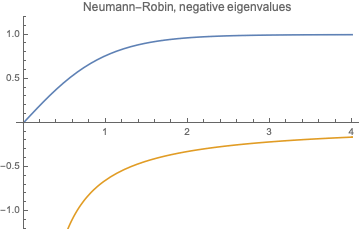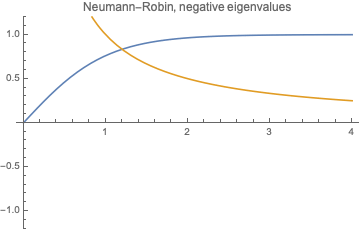
Let us find negative eigenvalues $\lambda=-k^2$ ($k>0$). We have $$X= A\cosh(k x) +B\sinh (k x). $$ Then $B=0$ and \begin{equation} \tanh (kl)=-\frac{\beta}{k}. \end{equation}
Solve it graphically: